SAFETY PROFILE
For adults with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP
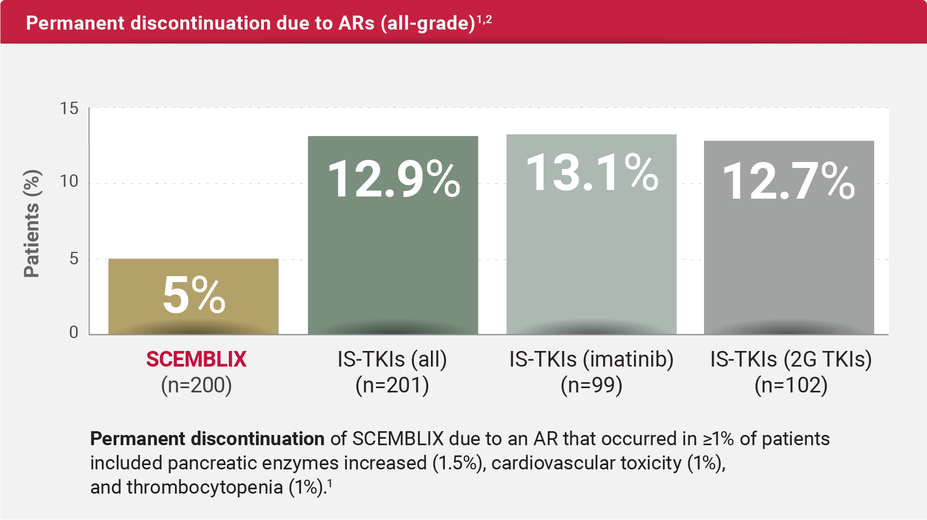
At Week 96, the discontinuation rate due to ARs was >2X lower with SCEMBLIX vs standard-of-care TKIs* (all)1,2
*Imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, and bosutinib.
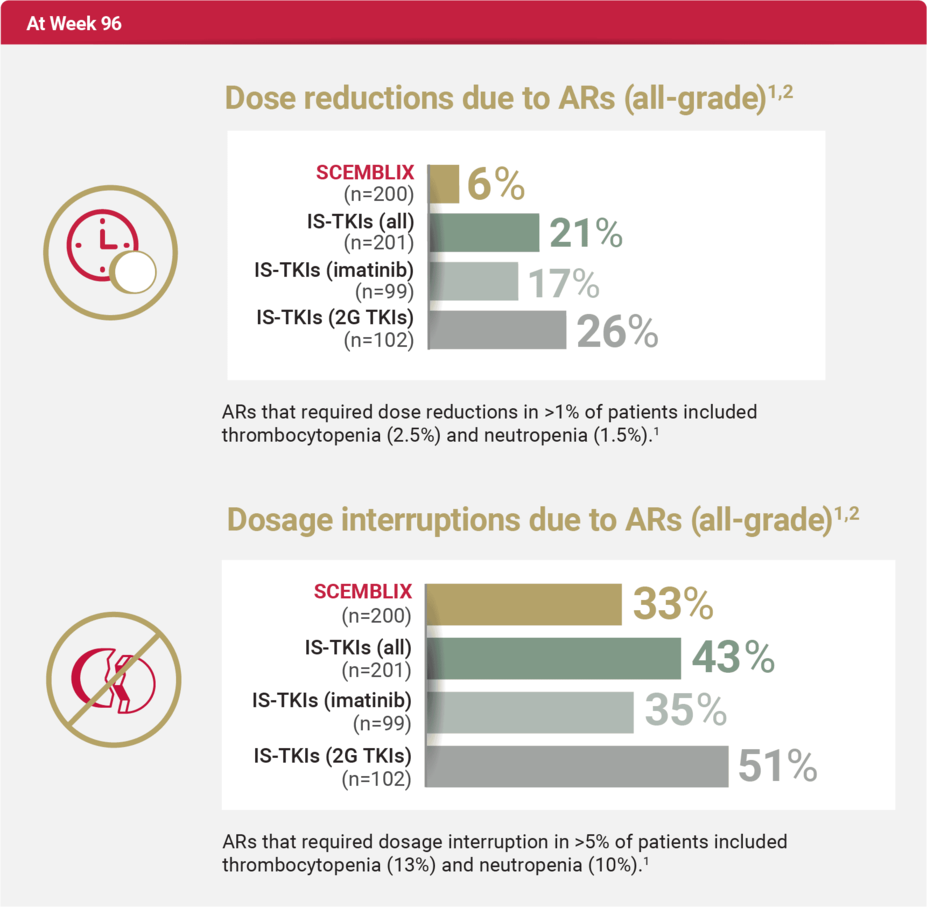
At Week 961,2
At Week 96, there were fewer dose reductions and interruptions due to ARs with SCEMBLIX vs standard-of-care TKIs (all)1,2
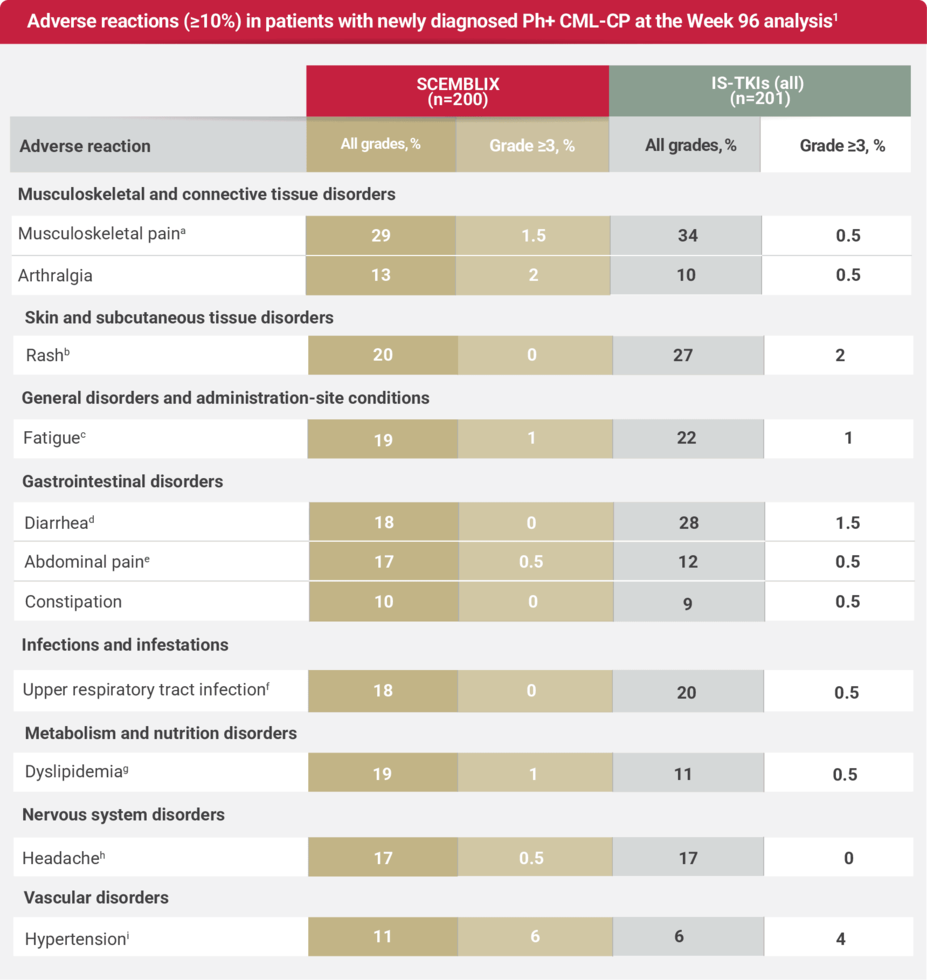
Safety profile at Week 961
aMusculoskeletal pain includes: musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, pain in extremity, back pain, non-cardiac chest pain, bone pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal chest pain, arthritis, and spinal pain.1
bRash includes: rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pustular, rash macular, dermatitis exfoliative, drug eruption, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, rash pruritic, and rash vesicular.1
cFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia.1
dDiarrhea includes: diarrhea, colitis, and enteritis.1
eAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, and gastrointestinal pain.1
fUpper respiratory tract infection includes: upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, and respiratory tract infection.1
gDyslipidemia includes: dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, blood cholesterol increased, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, and blood triglycerides increased.1
hHeadache contains: headache and migraine.1
iHypertension contains: blood pressure increased, blood pressure systolic increased, diastolic hypertension, and hypertension.1
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 15% of patients who received SCEMBLIX. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% included pancreatitis (1%), musculoskeletal pain (1%), and peripheral neuropathy (1%).1
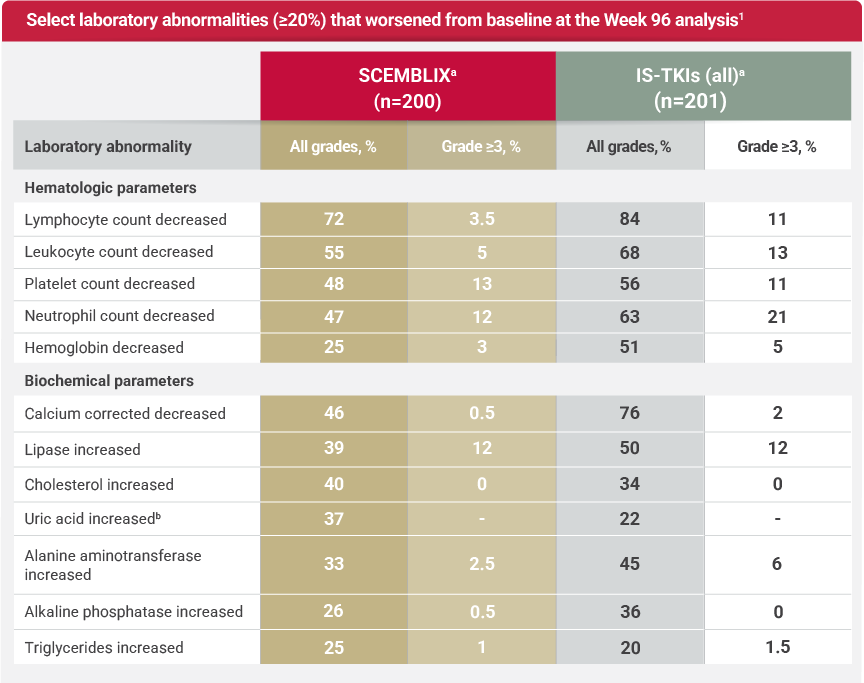
Laboratory abnormalities at Week 961
CTCAE version 5.0
aThe denominator used to calculate the rate for SCEMBLIX and IS-TKIs varied from 198 to 200 and 201, respectively, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least 1 posttreatment value.1
bWorst postbaseline laboratory abnormalities based on normal ranges.1
EXPANDED SAFETY PROFILE
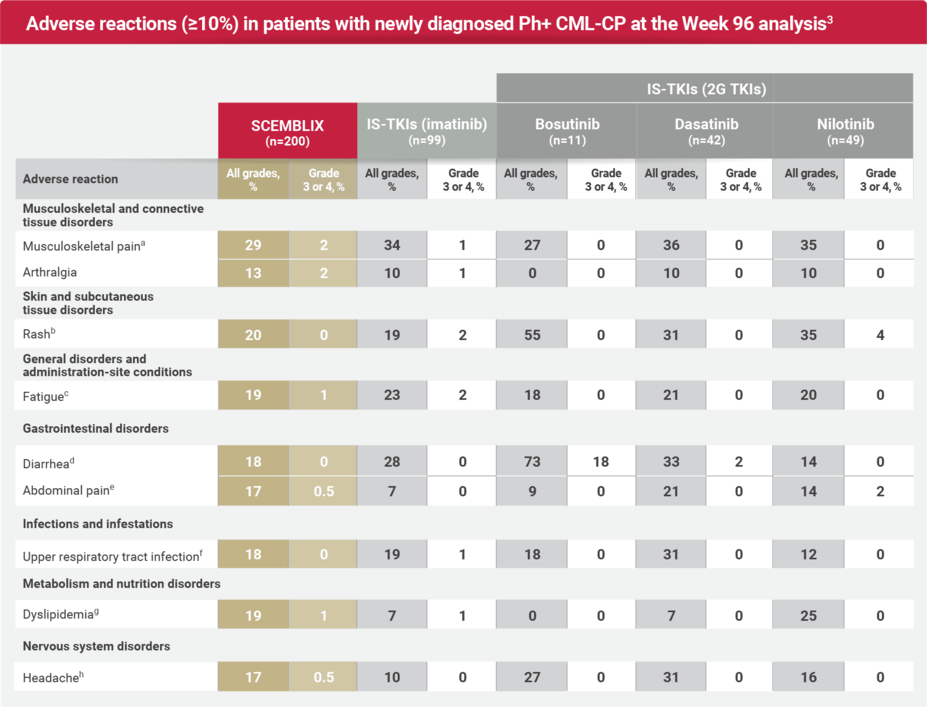
Safety profile: Expanded by standard-of-care TKIs at Week 963
aMusculoskeletal pain includes: musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, pain in extremity, back pain, non-cardiac chest pain, bone pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal chest pain, arthritis, and spinal pain.1
bRash includes: rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pustular, rash macular, dermatitis exfoliative, drug eruption, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, rash pruritic, and rash vesicular.1
cFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia.1
dDiarrhea includes: diarrhea, colitis, and enteritis.1
eAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, and gastrointestinal pain.1
fUpper respiratory tract infection includes: upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, and respiratory tract infection.1
gDyslipidemia includes: dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, blood cholesterol increased, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, and blood triglycerides increased.1
hHeadache includes: headache and migraine.1
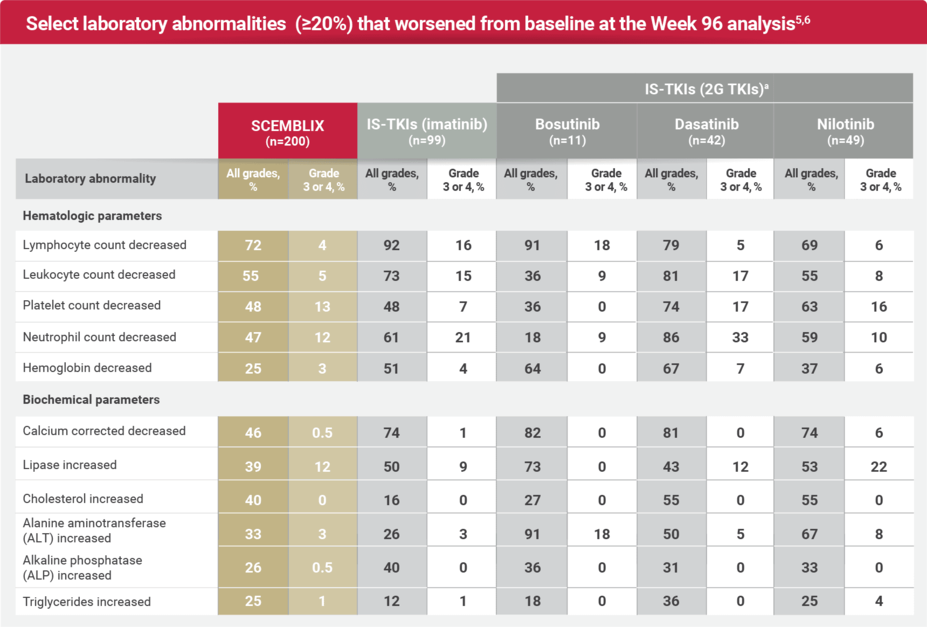
Laboratory abnormalities: Expanded by standard-of-care TKIs at Week 965,6
CTCAE version 5.0.
aThe denominator used to calculate the rate for SCEMBLIX and IS-TKIs varied from 198 to 200 and 201, respectively, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.1
2G, 2nd generation; AR, adverse reaction; CTCAE, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; IS-TKI, Investigator-selected tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Ph+ CML-CP, Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.