SCEMBLIX is also approved for adults with previously treated Ph+ CML-CP1
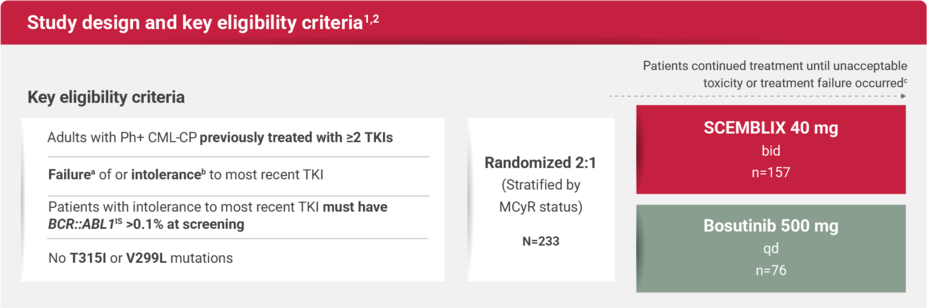
STUDY DESIGN
For adults with Ph+ CML-CP previously treated with 2 or more TKIs
ASCEMBL: The first 3rd-line+ Phase 3 trial in CML evaluating efficacy and safety vs a 2nd-generation TKI comparator1,2
Multicenter, randomized, active-controlled, open-label study1,2
Primary end point2
MMR rate at Week 24
Key secondary end point2
MMR rate at Week 96
Other select secondary end points2
Cytogenetic response rates and MMR rates, at and by scheduled data collection time points
Time to and duration of MMR
Time to and duration of CCyR
Safety and tolerability
Key baseline characteristics2,3
Resistance to last prior TKI: 61% of patients in the SCEMBLIX arm vs 71% with bosutinib3
Intolerance to last prior TKI: 38% of patients in the SCEMBLIX arm vs 29% with bosutinib2
MCyR at baseline: 29% of patients in the SCEMBLIX arm vs 29% with bosutinib3
Percentages of patients who had previously received 2, 3, 4, or 5 or more prior lines of TKIs were 48%, 31%, 15%, and 6%, respectively2
MMR was defined as BCR::ABL1IS ≤0.1%.1
CCyR was defined as 0% of Ph+ metaphases in bone marrow aspirate with at least 20 examined.1
MCyR was defined as 0% to 35% Ph+ metaphases.2
aMust meet the definition of treatment failure per the 2013 European LeukemiaNet recommendations. Patients meeting treatment failure criteria on bosutinib could be switched to SCEMBLIX.3
bDefined as nonhematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicity while on therapy; persistent grade 2 toxicity, unresponsive to optimal management, including dose adjustments; or hematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicity while on therapy, recurrent after dose reduction to the lowest recommended dose.4
cPatients will continue to receive study treatment for up to 96 weeks after the last patient’s first dose or 48 weeks after the last patient switches to SCEMBLIX, whichever is longer.4
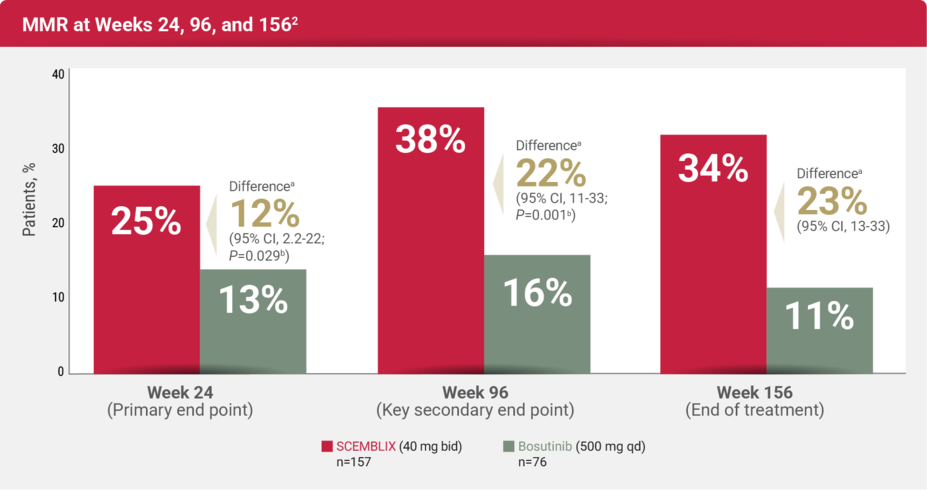
EFFICACY
For adults with Ph+ CML-CP previously treated with 2 or more TKIs
Response rates with SCEMBLIX at Week 24 and up to Week 156 (3 years) vs bosutinib1,2
The median duration of treatment was 156 weeks (range, 0.1 to 256 weeks) for patients receiving SCEMBLIX and 31 weeks (range, 1 to 239 weeks) for patients receiving bosutinib.2
The median duration of follow-up was 44 months.2
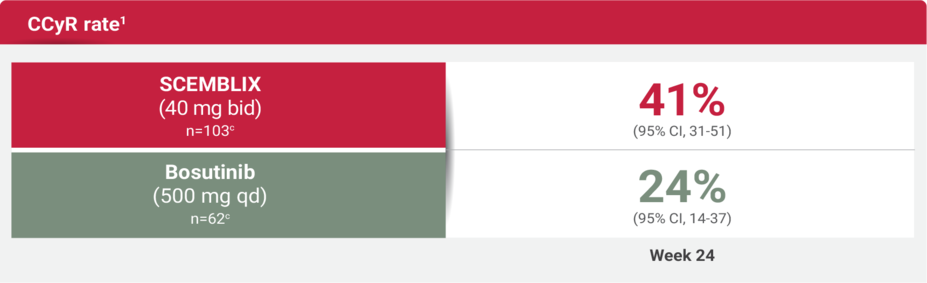
More patients achieved CCyR at Week 24 with SCEMBLIX vs bosutinib1
The CCyR rate at Week 96 was 40% (95% CI, 30-50) (n=103)c in patients receiving SCEMBLIX and 16% (95% CI, 8-28) (n=62)c for bosutinib. Note that any patient who achieved CCyR and later achieved MMR would not have been assessed for CCyR at Week 96. Of patients achieving CCyR during the study, 1 patient in the SCEMBLIX arm and 2 patients in the bosutinib arm lost response.1,2
aEstimated using a common risk difference stratified by baseline MCyR status.1
bEstimated using a Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel 2-sided test stratified by baseline MCyR status.1
cCCyR analysis based on patients who were not in CCyR at baseline.1
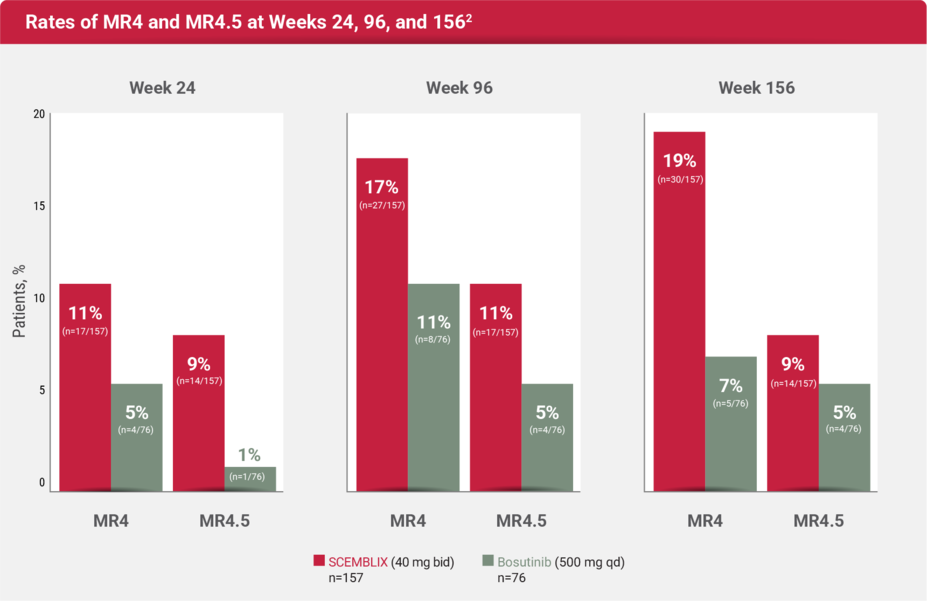
For adults with Ph+ CML-CP previously treated with 2 or more TKIs
MR4 and MR4.5 rates with SCEMBLIX vs bosutinib up to Week 156 (3 years)2,3
MR4 was defined as BCR::ABL1IS ≤0.01%. MR4.5 was defined as BCR::ABL1IS ≤0.0032%.3
SAFETY
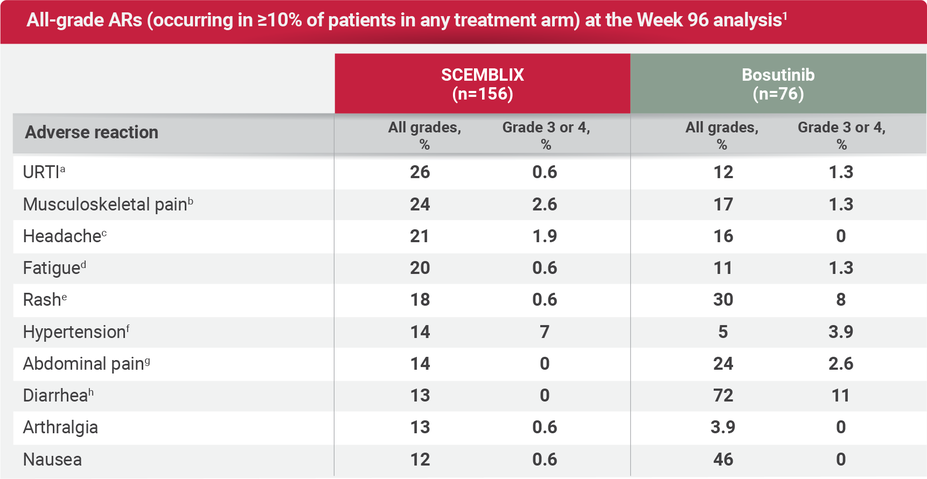
For adults with Ph+ CML-CP previously treated with 2 or more TKIs
The safety and tolerability profile of SCEMBLIX up to Week 156 (3 years)1,2,5,6
Rates of discontinuation with SCEMBLIX vs bosutinib
Week 961,5:
6% of patients on SCEMBLIX (n=10/156) required dose reduction due to adverse reactions vs 28% on bosutinib (n=21/76)
41% of patients on SCEMBLIX (n=64/156) required dose interruption due to adverse reactions vs 58% on bosutinib (n=44/76)
Week 1566:
6% of patients on SCEMBLIX (n=10/156) required dose reduction due to adverse reactions vs 28% on bosutinib (n=21/76)
42% of patients on SCEMBLIX (n=66/156) required dose interruption due to adverse reactions vs 58% on bosutinib (n=44/76)
For adults with Ph+ CML-CP previously treated with 2 or more TKIs
Well-established tolerability profile over time1,2
Serious ARs occurred in 18% of patients who received SCEMBLIX. Serious ARs in ≥1% included cardiac failure congestive (1.9%), pyrexia (1.9%), urinary tract infection (1.9%), headache (1.3%), and thrombocytopenia (1.3%). Two patients (1.3%) had a fatal adverse reaction, one each for mesenteric artery thrombosis and ischemic stroke.1
aUpper respiratory tract infection includes: nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, and pharyngotonsillitis.1
bMusculoskeletal pain includes: pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, bone pain, spinal pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, and musculoskeletal chest pain.1
cHeadache includes: headache and posttraumatic headache.1
dFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia.1
eRash includes: rash, rash maculopapular, dermatitis acneiform, rash pustular, eczema, dermatitis, skin exfoliation, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, rash morbilliform, drug eruption, erythema multiforme, and rash erythematous.1
fHypertension includes: hypertension and hypertensive crisis.1
gAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, abdominal tenderness, and epigastric discomfort.1
hDiarrhea includes: diarrhea and colitis.1
Discontinuation rate due to ARs was more than 3 times lower with SCEMBLIX vs bosutinib at Week 96 (8% vs 26%, respectively).2
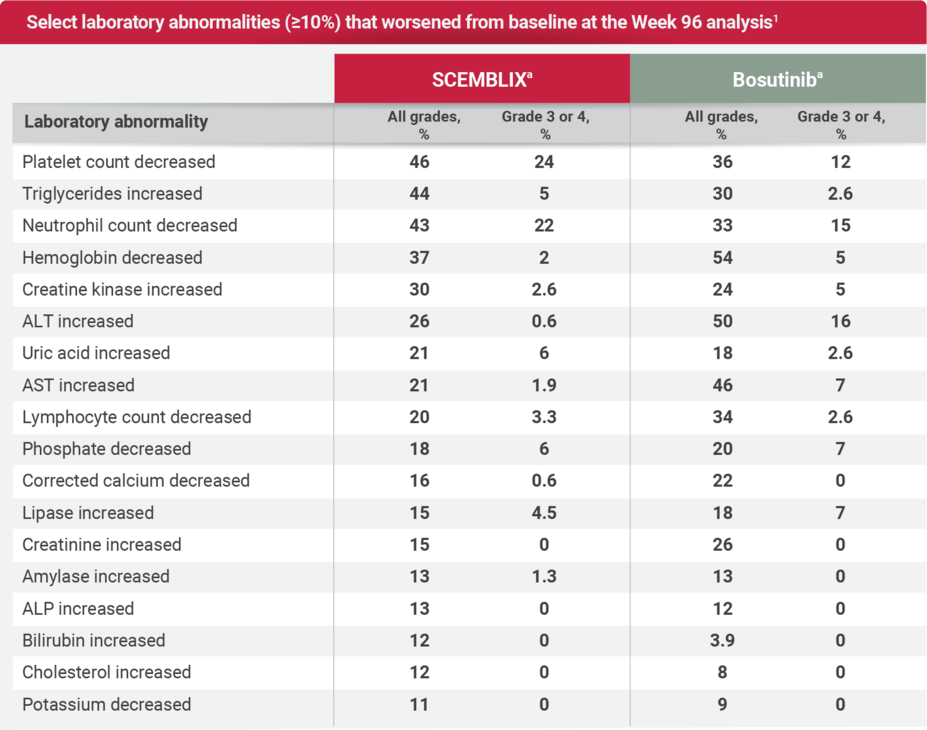
Laboratory abnormalities at Week 96 analysis1,2
The SCEMBLIX safety and tolerability profile at Week 96 was consistent and comparable overall to that of the Week 24 analyses, with no new or worsening safety findings.2
aThe denominator used to calculate the rate for SCEMBLIX and bosutinib varied from 152 to 156 and 75 to 76, respectively, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least 1 posttreatment value.1
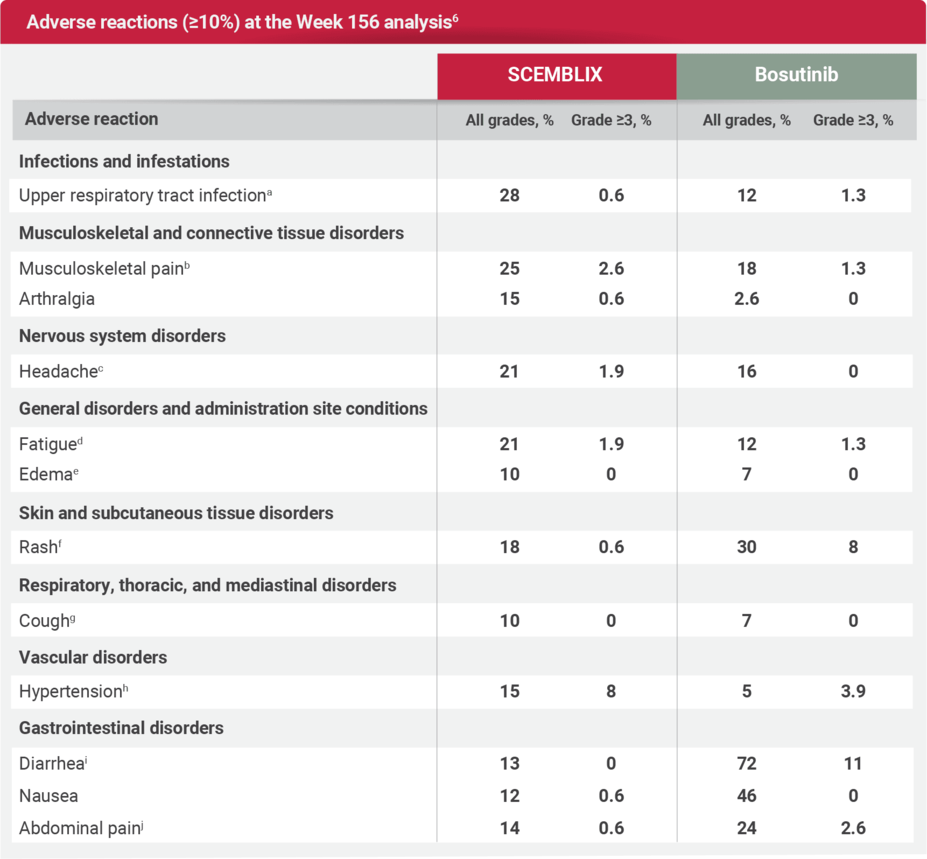
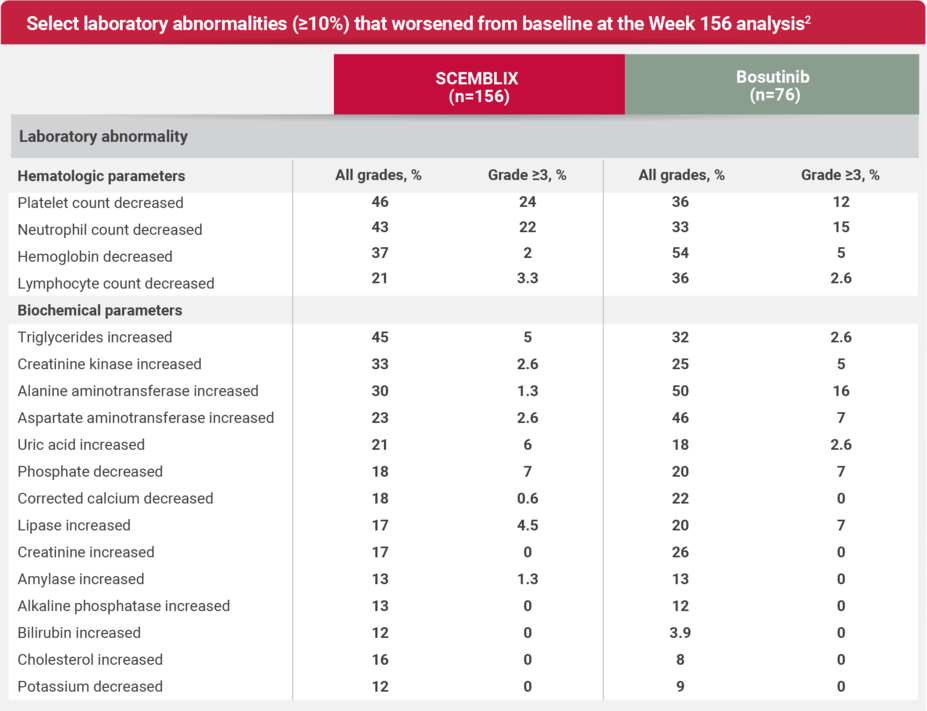
Safety profile at Week 156 (3 years) analysis6
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 22% of patients who received SCEMBLIX. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1%, included cardiac failure congestive (2.6%), pyrexia (1.9%), urinary tract infection (1.9%), arrhythmia (1.3%), headache (1.3%), and thrombocytopenia (1.3%). Four patients (2.6%) had fatal adverse reactions, one each for cardiac failure, mesenteric artery thrombosis, ischemic stroke, and one event with unknown cause.6
aUpper respiratory tract infection includes: nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, and pharyngotonsillitis.6
bMusculoskeletal pain includes: pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, bone pain, spinal pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, and musculoskeletal stiffness.6
cHeadache includes: headache, tension headache, migraine, and post-traumatic headache.6
dFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia.6
eEdema includes: edema, edema peripheral, localized edema, periorbital edema, face edema, swelling, and eyelid edema.6
fRash includes: rash, rash maculopapular, dermatitis acneiform, rash pustular, eczema, dermatitis, skin exfoliation, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, rash morbilliform, drug eruption, erythema multiforme, rash erythematous, and rash pruritic.6
gCough includes: cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome.6
hHypertension includes: hypertension and hypertensive crisis.6
iDiarrhea includes: diarrhea and colitis.6
jAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, abdominal tenderness, and epigastric discomfort.6